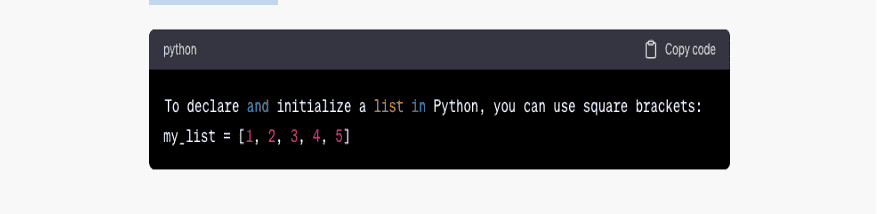
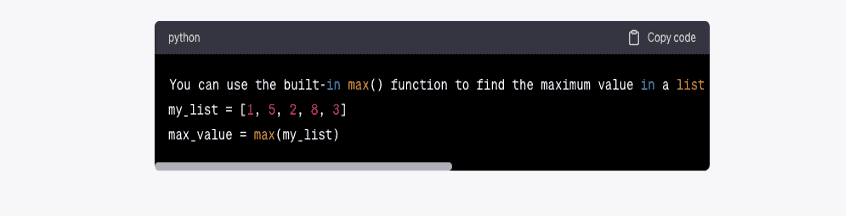
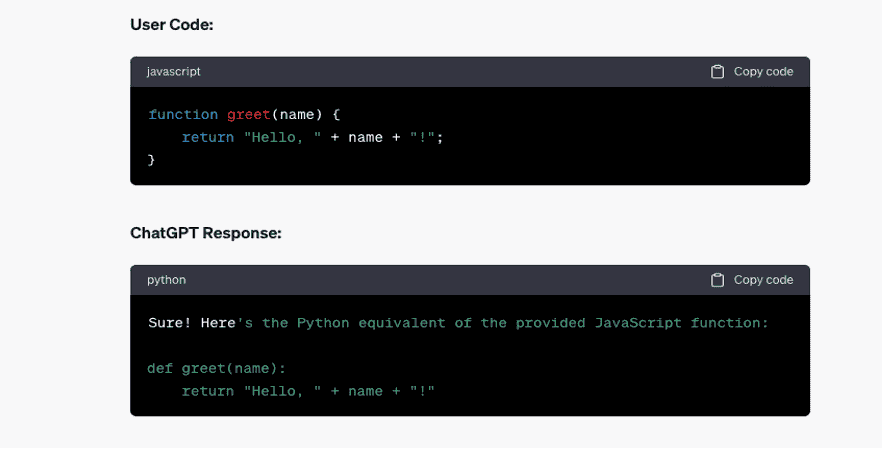
In this article, we will explore ten ChatGPT prompts specifically tailored to boost productivity for programmers. By incorporating these prompts into your daily routine, you can overcome challenges, stimulate your creativity, and enhance your overall programming experience.
In today’s fast-paced programming landscape, leveraging artificial intelligence tools such as ChatGPT prompts can significantly enhance your productivity. ChatGPT is a language model designed to assist you in various aspects of programming, offering suggestions, explanations, and problem-solving assistance. By incorporating ChatGPT prompts into your daily routine, you can streamline your coding process, overcome challenges, and discover innovative solutions.
7 Benefits of Using ChatGPT for Programmers:
1. Instant Code Assistance-
ChatGPT serves as an instant coding companion, providing programmers with quick answers to syntax-related questions. Whether it’s the correct syntax for a language or a specific library, programmers can rely on ChatGPT for accurate and on-the-spot assistance.
2. Debugging Support-
Debugging code can be challenging and time-consuming. ChatGPT can help programmers identify potential bugs and suggest possible solutions, saving valuable debugging time and efforts.
3. Algorithmic Optimization-
Optimizing algorithms is crucial for efficient code execution. Programmers can seek ChatGPT’s advice on algorithmic improvements, enabling them to enhance the performance of their code.
ChatGPT can generate code snippets based on specific requirements, helping programmers expedite their development process. Whether it’s creating a function or a complex data structure, ChatGPT can provide ready-to-use code, reducing manual coding efforts.
For programmers working with multilingual codebases, ChatGPT can assist in translating code between different programming languages. This feature facilitates code reuse and collaboration among developers using diverse languages.
Refactoring code is essential for maintaining code quality and readability. ChatGPT can suggest ways to refactor complex code snippets, helping programmers write cleaner and more maintainable code.
ChatGPT can provide guidance on integrating various frameworks and APIs effectively. Whether it’s interacting with web APIs, databases, or third-party libraries, programmers can rely on ChatGPT’s advice for smooth integration.
In JavaScript, the map() function is a higher-order array method that operates on an array and allows you to transform each element of the array into a new value. It creates a new array containing the results of applying a provided function to each element of the original array without modifying the original array.
The map() function takes in a callback function as an argument. This callback function is executed once for each element in the array, and its return value becomes the corresponding element in the new array. The original array remains unchanged.

Here’s the syntax of the map() function:
Parameters:
array: The original array on which you want to apply the map() function.
callback: A function that is called for each element in the array. It can take three parameters:
currentValue: The current element being processed in the array.
index (Optional): The index of the current element being processed.
array (Optional): The original array being processed.
The map() function iterates over each element of the array and applies the callback function to each element, passing the element, index (optional), and the original array (optional) as arguments. The return value of the callback function is collected in a new array, which is then returned by the map() function.
Here’s an example of how the map() function works:
In Example 1, each element of the numbers array is doubled, and the resulting array doubledNumbers contains the doubled values.
In Example 2, the squaredNumbers array is created by squaring each element of the original numbers array.
In Example 3, the indexedNumbers array is obtained by multiplying each element of the numbers array with its corresponding index incremented by 1.
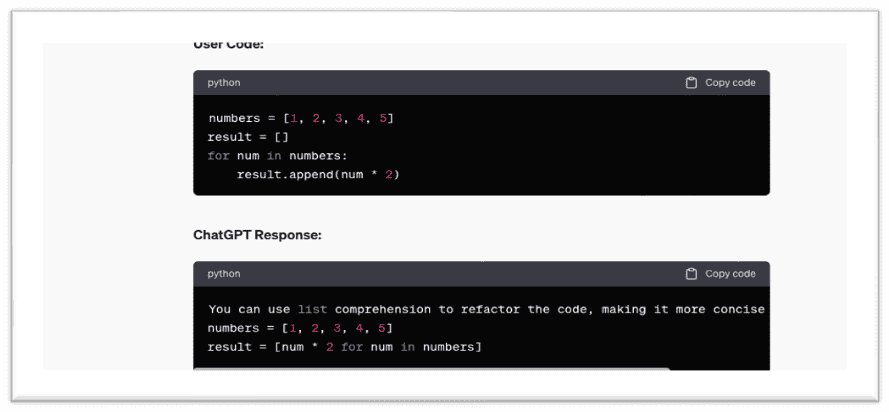
Prompt 2: Optimize the Code